RESTrade
The RESTrade module presented in the web tool comprises the models of the traditional power and energy balancing markets updated in the TradeRES project considering existing and newly proposed market designs. This module supports the participation of actors as conventionally dispatchable power plants, vRES - variable renewable energy systems, and demand players in the system balance, contributing to the automatic (aFRR) and manual (mFRR) frequency restoration reserve markets, also known as secondary and tertiary reserves. Additionally, it may use both the marginal pricing theory and the pay-as-bid scheme to define clearing prices for reserve trading.
The aFRR power capacity requirements are computed considering the balancing guidelines of the ENTSO-E. It can also be computed as in the Portuguese system or using dynamic reserves. Dynamic reserves consider the separate procurement of upward and downward power capacity considering forecasts of both demand and variable renewable generation.
Furthermore, the system also computes the MIBEL imbalance settlement based on the Portuguese, Spanish, or a newly proposed formulation within TradeRES. The Portuguese formulation considers that all Balance Responsible parties (BRPs) must pay the energy used to balance the system equally. So, it computes a single penalty and dual pricing. The Spanish formulation computes the balance direction and only the BRPs that originate those balance needs must directly pay/receive the price of the energy used to balance the system. The new TradeRES formulation considers that BRPs only pay the price of the required energy to balance their deviations. So, it considers double pricing and penalties without economic surplus or deficit to system operators.
New market designs of balancing markets consider: i) the separate procurement of upward and downward capacity; ii) smaller volumes; iii) gate closures closer to real-time operation, and iv) shorter market time units. These changes to current market designs favor the active participation of variable renewable generation and smaller players.
The RESTrade module is integrated with MASCEM in Spine Toolbox. It requires to run previously the MASCEM models as indicated in the following chart:
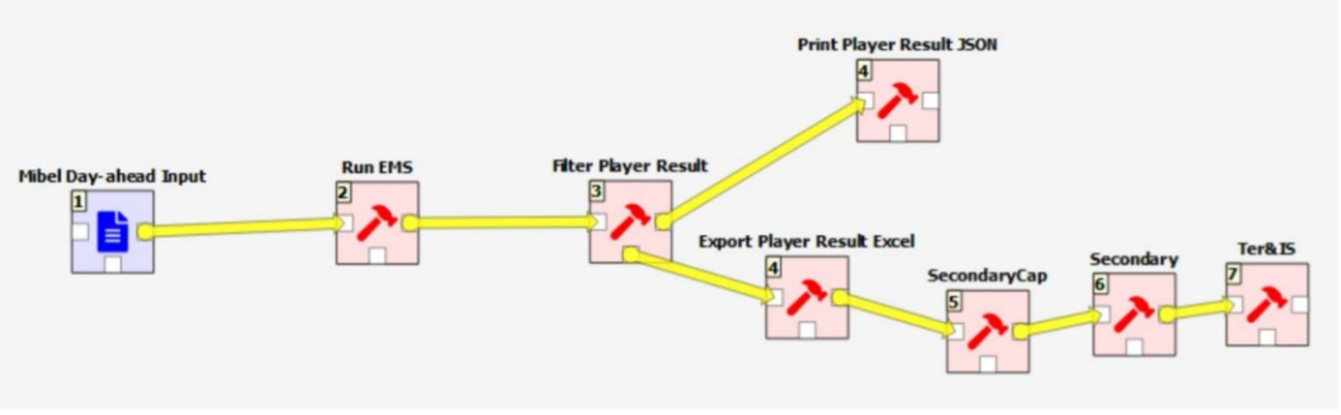
RESTrade consists of the following blocks: “SecondaryCap”, “Secondary” and “Ter&IS”, which are used to simulate the i) secondary capacity, ii) secondary energy and iii) the tertiary energy and imbalance settlement markets, respectively.
A complete simulation of the Iberian power systems can be performed using three different simulators provided in the project (Backbone, MASCEM and RESTrade), as illustrated in the following chart:
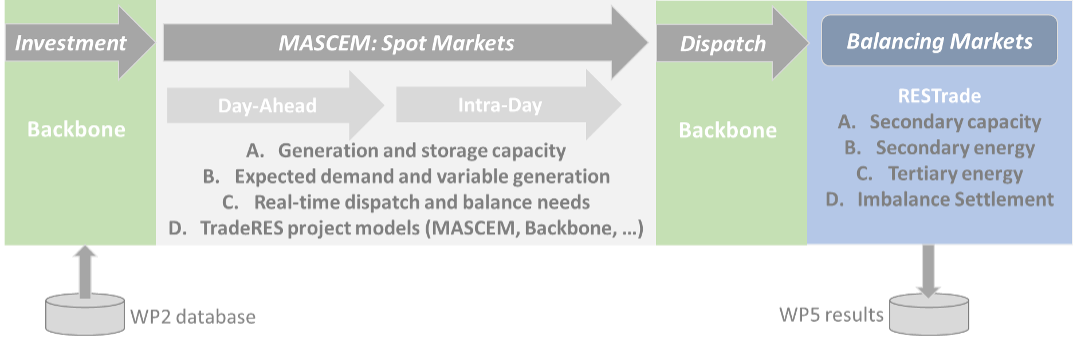
Backbone allows us to simulate long-term optimal investments in Europe, providing new production and storage capacities. These capacities are then used to equip the agents with the capability to participate in the MASCEM's short-term spot markets and RESTrade's market of ancillary services. Backbone also simulates the real-time optimal dispatch considering sector coupling. It computes the real-time energy values of hydrogen, batteries, and pumped hydro storage.